Help
How to use
DARUMA is designed to process a large number of sequences rapidly, and users can select the input type, single sequence or multiple sequences, in the query type check box. After selecting the query type, paste an amino acid sequence(s) or select a file containing the sequence(s). The sequence(s) must be in the FASTA format in both cases. If user select Multiple in the query type check box, a text box will appear where the user should enter the email address to receive the results. Press the submit button, and DARUMA returns the results in a few seconds for a single sequence query. In the case of multiple sequences, the URL of the Result page will be sent by email.
Output format
Single sequence query.
DARUMA gives a graphical result for a single sequence query. The line plot in blue indicates the disorder probability for each residue. The orange bars represent the predicted disorder regions which show the probability greater than 0.5.
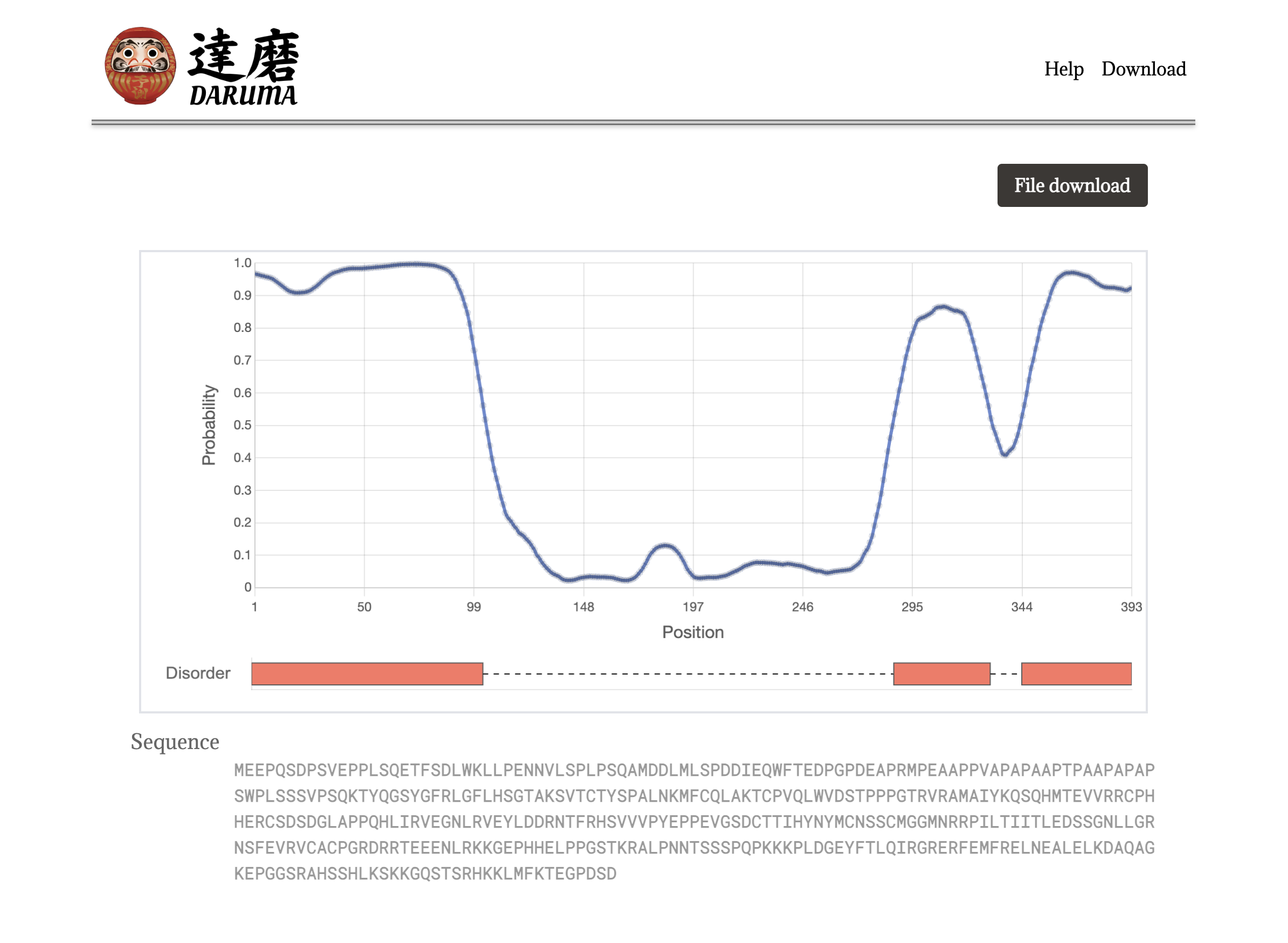
The user also can have the result in a text format by clicking the File download button at the upper right section. An output file is created for each protein, and the accession is used for the file name. When any characters of ⌘, /, *, ? , :, ”, <, >, and | are used in the accession, they are replaced with an underscore.
The text output format is as follows: the accession is shown on the first line followed by the lines consisting of position index, residue, probability, and a digit, where 0 and 1 represent ordered and disordered. An example of the result is shown below.
>sp_Q6ZWJ8
1 M 0.9710 1
2 A 0.9687 1
3 G 0.9670 1
Multiple sequence query.
When the user submits a multiple FASTA file, DARUMA returns an email containing the URL linked to the result page.
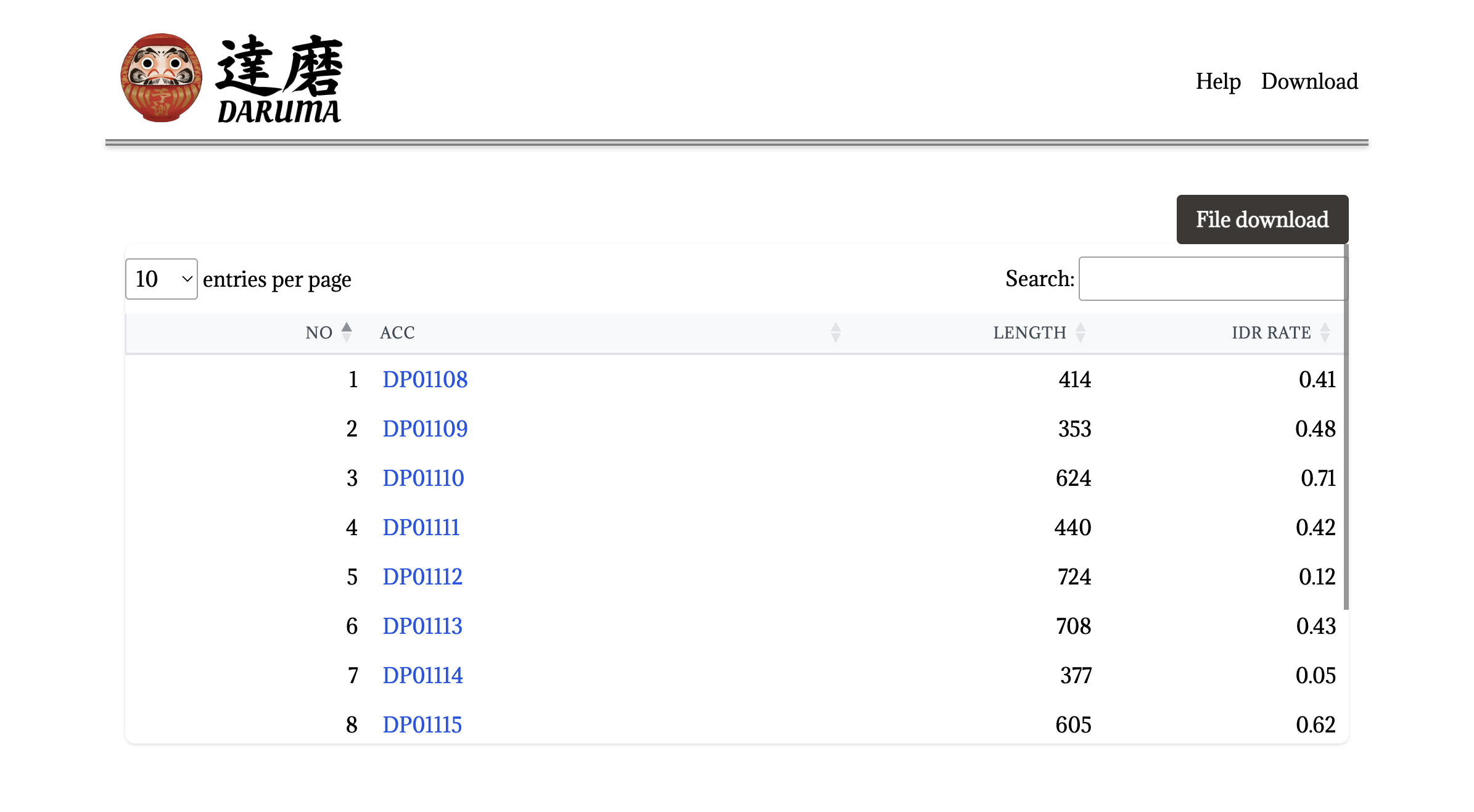
Each line is linked to the graphical result page for a protein illustrated above. Clicking the File download button also allows the user to download a zip file containing all of the results in the separate files.
Prediction method
DARUMA predicts the disorder probability of each residue of a protein and classifies the amino acid sequences into disordered or ordered. DARUMA employs a combination of convolutional neural networks and conventional neural networks.
The brief data proceeding flow of DARUMA is as follows:
1. Protein sequences are embedded into a feature vector by using the 553 physicochemical properties of amino acids from the AAindex database.
2. The structure of DARUMA model is composed of two units: a feature extraction unit (FEU) consisting of three one dimension convolutional layers, and a prediction unit (PU) consisting of two fully connected layers. A protein sequence embedded with AAindex is passed through the FEU and PU, and the predicted probability of each residue is calculated. PU considers the peripheral features around the residue in interest by accepting a set of feature values of 121 residues centered with the residue in interest.
3. PU gives a binary probability, disordered and ordered, of each residue for the entire sequence, and the probabilities are smoothed over 17 residues centered with the residue in interest, leading the final disorder probability for the residue.
4. Residues with a probability greater than 0.5 are classified as Disorder, and the others as Order. After this classification, disorder regions shorter than 10 residues are converted to Order, and order regions shorter than 10 residues are converted to Disorder.
